In the financial services industry, data is the lifeblood that drives decision-making, customer engagement, and operational efficiency. However, the vast amounts of data generated across various systems often remain isolated in silos, creating fragmented views that hinder strategic initiatives. To unlock the full potential of their data, financial institutions must employ effective data integration techniques that unify these disparate systems into a cohesive, accessible, and actionable resource.
The Role of Data Integration in Financial Services
Data integration involves consolidating data from multiple sources, such as databases, cloud services, and legacy systems, into a unified format that allows for seamless data management and analysis. For financial institutions, this process is crucial as it enables the extraction of valuable insights from scattered data, supporting everything from fraud detection to customer personalization.
Consider a bank with separate systems for customer relationship management (CRM), transaction processing, and risk management. Each system houses critical data, but without integration, these data sets remain disconnected, leading to inefficiencies and missed opportunities. By integrating data across these systems, the bank can gain a comprehensive view of its operations, enhancing its ability to make informed decisions and deliver superior services.
Key Benefits of Data Integration
Improved Decision-Making
Data integration enables financial institutions to combine real-time data from various sources, allowing for quicker responses to market changes and more agile business strategies. For instance, by integrating data from trading platforms and customer analytics, brokers can better understand market trends and client preferences, leading to more accurate investment decisions. This holistic approach ensures that decision-makers have access to the most relevant and timely information, ultimately driving better outcomes.
Enhanced Customer Experience
In today’s competitive landscape, delivering exceptional customer experiences is paramount. Data integration allows financial institutions to achieve a 360-degree view of their customers by consolidating data from multiple touchpoints, including CRM systems, social media, and transaction records. This integrated view enables the delivery of personalized services, tailored financial advice, and more meaningful customer interactions, all of which contribute to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Operational Efficiency
Operational efficiency is a key driver of profitability in the financial services industry. Data integration streamlines processes by reducing data redundancy and ensuring consistency across systems. For example, integrating data from different financial platforms can eliminate the need for manual data entry and reconciliation, significantly reducing the risk of errors and saving valuable time. This efficiency allows financial institutions to focus on more strategic initiatives, such as innovation and customer engagement.
Enhanced Risk Management
Risk management is a critical component of financial services, and data integration plays a vital role in improving risk assessment and mitigation. By integrating data from various sources, such as credit scoring systems, market data, and transaction histories, financial institutions can develop more accurate risk models and identify potential threats more effectively. This integrated approach not only enhances the institution’s ability to manage risks but also ensures compliance with regulatory requirements.
Greater Business Agility
In an industry where market conditions can change rapidly, business agility is essential for maintaining a competitive edge. Data integration empowers financial institutions to adapt quickly to these changes by providing real-time insights into market trends, customer behavior, and operational performance. This agility allows institutions to launch new products and services, respond to customer demands, and capitalize on emerging opportunities with confidence.
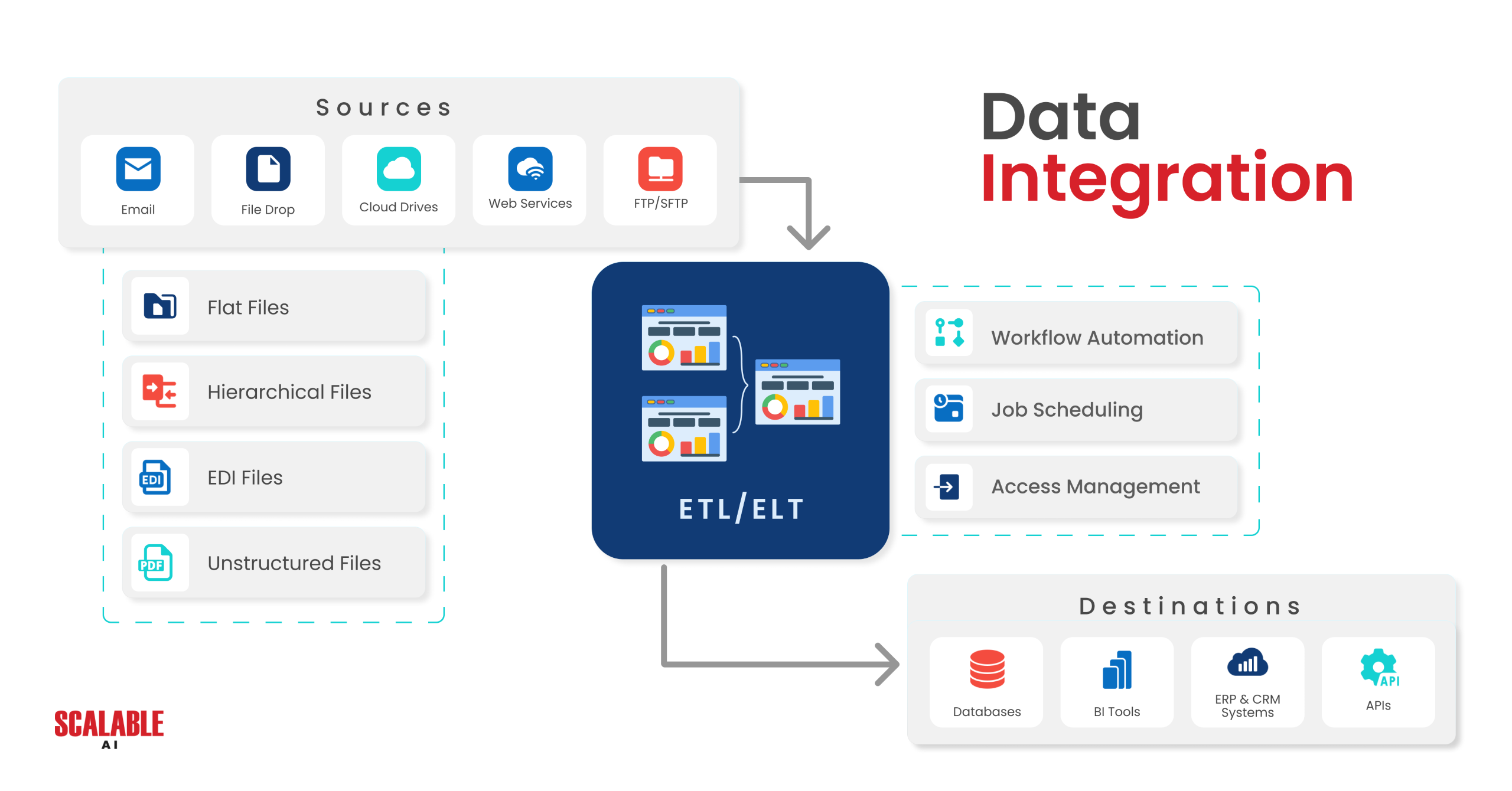
Techniques for Effective Data Integration
To achieve these benefits, financial institutions must employ the right data integration techniques. The choice of technique depends on the specific needs of the organization, the nature of the data, and the systems involved.
Extract, Transform, Load (ETL)
ETL is a traditional data integration method that involves extracting data from various sources, transforming it into a suitable format, and loading it into a target system, such as a data warehouse. This method is particularly effective for consolidating historical data and preparing it for business intelligence (BI) applications. However, ETL’s batch processing nature can introduce latency, making it less suitable for real-time integration needs.
Extract, Load, Transform (ELT)
ELT is a variation of ETL where data is first extracted and loaded into the target system before being transformed. This approach leverages the computational power of modern data warehouses, allowing for more flexible and scalable integration processes. ELT is particularly useful for big data analytics and scenarios where raw data needs to be stored for future analysis.
Middleware and Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS)
Middleware and iPaaS solutions offer platforms for connecting and synchronizing data between different systems. These solutions often come with pre-built connectors and integration workflows, reducing development time and complexity. Middleware and iPaaS are ideal for cloud integration scenarios where on-premises and cloud applications need to be connected, providing a unified platform for both real-time and batch data integration.
API Integration
API integration enables real-time data exchange between systems using Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). This method is highly flexible and supports secure, scalable, and real-time data synchronization. API integration is particularly useful for connecting SaaS applications and enabling mobile apps to interact with backend services, providing seamless access to up-to-date information.
Data Virtualization
Data virtualization allows applications to access and manipulate data from various sources without moving or replicating the data. This technique provides a unified view of data across the organization, simplifying data access and management. Data virtualization is especially useful for real-time analytics and scenarios where data needs to be aggregated from multiple sources for comprehensive reporting.
Conclusion
Data integration is no longer a luxury but a necessity for financial institutions aiming to thrive in a data-driven world. By unifying disparate systems and enabling seamless data flow, financial institutions can unlock the full potential of their data, driving improved decision-making, enhanced customer experiences, and greater operational efficiency. As the financial services industry continues to evolve, the adoption of robust data integration techniques will be critical to staying competitive, compliant, and customer-centric in an increasingly complex and dynamic market.
Read Whitepaper Data Dilemmas: Solving Financial Services Challenges
