The telecom industry continues to generate more and more information as new technologies like 5G are introduced and the number of connected devices rises. Telecommunications companies need to leverage big data to maximize its worth if they want to survive in a data-driven world. Organizations can use big data analytics to improve services, increase revenue, and develop a more customer-centric strategy to stay ahead of the competition.
Conventional data has a more structured format, maintains a lower volume, and allows easy access through normal databases and tools. In contrast, big data presents far more intricacies. It encompasses large datasets composed of various types of information—structured, unstructured, and semi-structured—that are gathered from diverse sources.
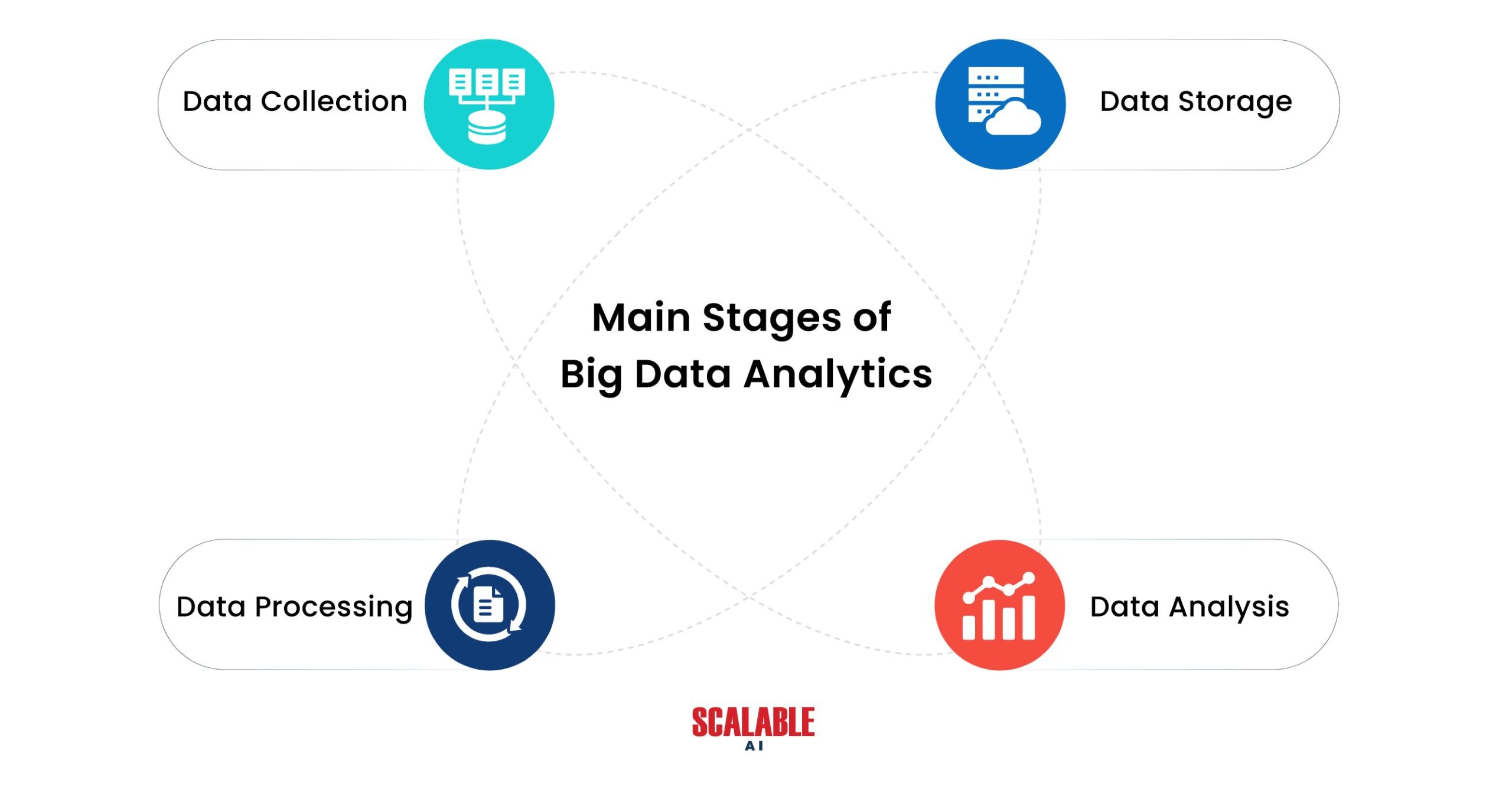
The main stages of big data analytics are:
Data Collection: Analysts get data from multiple sources, both structured and unstructured.
Data Storage: To facilitate future information management, the gathered data is kept in a data lake or data warehouse.
Data Processing: Involves transforming, cleaning, and integrating the data to guarantee that it is in an appropriate format for analysis.
Data Analysis: The procedure uses a variety of methods (such as data mining and machine learning) to examine and glean insightful information from complicated data.
Understanding the Importance of Telecom Analytics
The typical telecom firm routinely collects vast amounts of data. This data gives important insights into network operations, client behavior, equipment condition, and service quality. However, because of numerous problems, a large amount of this data is either erroneous or remains unusable. Organizations find it challenging to fully utilize its potential. Ineffective analytics can lead to unhappiness, mistrust, and poor customer service.
To maximize their information, telecom businesses integrate big data analytics into their operations. They minimize their pain points and forecast future results by using analytics to gather, analyze, and understand information thoroughly. This enhances decision-making both now and in the future. Precedence Research projects that the telecom analytics industry will grow from $6.19 billion in 2022 to $23.66 billion in 2032.
Challenges Faced by the Telecom Sector in Big Data Analytics
Telecom businesses may undoubtedly gain a great deal from employing big data sets, but there may be certain challenges to overcome when using data analytics.
Diverse Data Sources
Telecom companies get information from a variety of sources, such as network logs, call detail records, client histories, etc. Information is produced by each source using various protocols, structures, and formats. As a result, efficiently integrating and analyzing this data becomes a difficult operation that calls for particular processing methods and equipment. The old systems that telecom businesses frequently use may not be compatible with some contemporary data formats or integration techniques. As such, it presents difficulties in maintaining consistency, quality, and administration of data.
Because of this, businesses must spend money on reliable and expandable data integration solutions. It facilitates the standardization of data and increases its accessibility and analytics-friendliness.
Several, Isolated Data Sources
The telecom sector is a global industry that operates across multiple nations and areas. As a result, data is typically not centralized and is instead dispersed over several physical and digital sites. As a result, a lot of telecom firms keep their data in separate systems or silos. There are several reasons why these data silos occur, including the use of data by distinct departments, the existence of legacy systems, or the lack of integration plans.
Data Inconsistencies
Telecom data frequently has quality problems, including missing numbers, inconsistent data, and inaccurate data. Network faults and integration challenges are just two of the many causes of data quality problems. For instance, inaccurate client information or missing values in call logs can compromise the analysis’s dependability and correctness.
Data Preparation
Much of the collected information needs preprocessing, cleaning, and transformation before it can be used for analytics. For this reason, data cleaning and preparation can be a labor-intensive, time-consuming, and costly process. Errors are frequently made, and the final data quality may not always be up to par. The amount of data that analytics must evaluate is always growing, requiring them to examine large datasets. The difficulty is exacerbated as data volume increases.
High Costs
Large and complicated data sets provide many potentials for the telecom industry to grow, but managing these advantages costs a lot of money. Businesses must properly organize their resources and finances to handle vast amounts of data. Telecommunications firms must invest in integrating and maintaining a dependable infrastructure, fixing broken equipment, introducing cutting-edge technology, and recruiting skilled personnel.
Poor Customer Service
In the telecom industry, customers frequently experience bad service due to the constantly evolving industry and their changing expectations. Various issues contribute to this problem, such as poor call center assistance, sluggish data transfers, inaccurate billing, and technical issues. Inadequate analysis can also harm customer service, damaging the company’s reputation and fostering consumer mistrust and lack of loyalty.
Network Failures
Numerous factors can cause network outages, including hardware malfunctions, cyberattacks, natural disasters, and technological issues. For a big data project to succeed, a dependable and steady network connection is necessary. Any interruption in network connectivity could result in risks, processing lags, or data loss. Therefore, if businesses lack reliable software and a solid network, they may face concerns such as poor performance or security vulnerabilities.
Use Cases of Telecom Data Analytics
In addition to finding solutions for the above mentioned problems, the telecom sector also discovers incredible chances to fully utilize its information. These are a few of the most interesting applications of telecom network analytics.
Enhanced Customer Experience
Gaining and retaining consumers depends on having a thorough grasp of their wants and behaviors. Consider this: your telecom provider supplies you with what you need since they are aware of your particular needs. How precisely is it real, though? Telecom businesses examine data from phone logs, usage trends on the Internet, and geographic data. They then use analysis to build comprehensive consumer profiles and offer tailored promotions and services.
Customer Churn Prediction
Telecom firms may identify customer churn threats with the use of predictive analytics, which is powered by big data. Predictive analytics enables businesses to continuously monitor and handle any issues with their services and make smart decisions to retain customers, regardless of the cause—whether it’s network problems or subpar customer service.
Network Optimization
The optimization of network efficiency, dependability, and performance is another illustration of how analytics may be used effectively. By evaluating data from network equipment, user devices, and other sources, telecom businesses can greatly enhance their network operations. Telecom providers can detect network bottlenecks and congestion as a means of minimizing downtime and guaranteeing uninterrupted data delivery.
Fraud Detection
Telecom companies are particularly vulnerable to fraud due to their intricate networks and large volume of transactions. Interconnection bypass fraud, SIM switching, and account seizures can jeopardize a telecom business’s financial stability, costing the company millions of dollars annually. In the telecom sector, criminals pose a major threat through International Revenue Share Fraud (IRSF).
Predictive Maintenance
To avoid downtime during service delivery, telecom businesses must continuously monitor the status of their equipment and ensure network resilience. They can analyze environmental conditions, equipment conditions, and network performance through analytics. Using this method, telecom providers can identify abnormalities and early warning indicators that precede failures and determine the causes of the problems.
Cost Optimization
The telecom sector must manage various operating expenses, including labor and network maintenance. Telecom businesses use analytics as a tool to understand their operating costs and identify areas where they can cut expenses. For instance, analytics can track energy usage throughout the network architecture. Telecom carriers can optimize energy-intensive areas, saving a significant amount of money on energy costs.
Customer Segmentation
Telecommunication companies segment their consumer base using increasingly complex techniques as they produce more data. Companies now consider phone logs, surfing histories, and social media activity alongside more conventional data sets such as demographics, age, and location to gain more advanced insights. Additionally, businesses can fully comprehend client wants through deep learning.
Target Marketing
One of the telecom network solutions enhances marketing campaign effectiveness. Telecom companies utilize big data to track marketing campaigns in real-time. Analytics enables companies to create a complete plan to enhance marketing campaigns by segmenting clients based on their comments, service preferences, and past purchases. They can quickly optimize poorly performing campaigns, which boosts conversion rates and lowers expenses.
Customer Lifetime Value Prediction
In today’s competitive market, customers are constantly seeking the best value, making it easy for them to switch to competitors. To mitigate this, telecom providers use analytics to accurately predict customer lifetime value (CLV). Using machine learning models, historical data, and segmentation, CLV is forecasted for each customer. In these models, a variety of factors are considered, such as customer longevity, service usage, average revenue per user (ARPU), and churn likelihood.
Conclusion
It is only a matter of time until telecom analytics becomes widely used; it is an invaluable tool. The above mentioned data analytics use cases—which range from enhanced customer support and network efficiency to predictive results—have already changed the way telecom businesses conduct business. As a result, the deep integration of big data is the future of telecom firms, as it will drive an increasingly customer-focused and efficient sector.
Read Whitepaper Telecom’s Treasure Trove: Mining Customer Insights from Big Data
