There is a lot of data in the telecom industry. We are discussing the generation of terabytes, if not petabytes, of data every day concerning service utilization, network performance, and consumer data. Every telecom eventually must deal with the problem of interpreting all this data. Fortunately, data mining provides a solution. Truth be told, data mining isn’t just confined to telecom. Many industries have adopted it as a method, producing amazing outcomes. Remarkably, 90% of businesses that mine big data are making substantial profits. Experts predict that gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data will transform various industries, including telecom. We would like to share our understanding of data mining in the telecom sector in this blog. Continue reading to find out more about how using data mining can help your company and provide you with useful information.
Types of Data in the Telecom Industry
The three primary forms of B2B and B2C data that are thought to be the most important ones in the telecoms industry are customer, network, and call-detail data.
Call-detail Data:
Telcos own vast amounts of data regarding the phone calls made by their clientele. This information comprises phone numbers that people call and receive, the duration of the calls, the time they were made, and occasionally even the location of the calls.
An analysis of all this call data can reveal some fascinating insights for a telco. For instance, they can discover which locations receive the most calls from their clientele. Certain clients may have partners or customers in particular nations or cities. The data mining method uses this information to better understand the calling habits and preferences of telecom service users.
The busiest call hours can also be determined by telcos. Businesses can discover, for example, that most of their clients contact a lot in the morning to arrange meetings or talk about significant issues by employing data mining. Telcos can avoid delays and poor call quality by making sure their phone lines are ready to handle the increased call volume at the busiest hours.
And here’s the most exciting part: telcos can use all this information in the data mining process to improve customer loyalty. For example, with data mining, telcos can learn that many of their clients call a specific country a lot, and offer calling plans that fit their customers’ preferences and let them save costs. Personalized offers make users understand that the telco they chose does care about them, so they want to stick around and enjoy the benefits.
Network Data
Network data provides information about the quality of calls, data throughput, network congestion, and other crucial network characteristics.
Telcos can determine any problems or blockages in their network by examining network data. For instance, a telecom provider may find that some locations have weak signals or are frequently congested at particular times of the day. With this understanding, they can troubleshoot and take the appropriate action to enhance network performance, giving their business clients a faster and more seamless internet experience.
Additionally, the business can forecast network consumption patterns by mining network data. For instance, they might notice that there is a significant demand for bandwidth during business hours because of an increase in online activity. Equipped with this knowledge, they may allocate resources where they are most required to improve their network architecture and guarantee that companies have enough bandwidth to run smoothly.
Customer Data
Personal information including names, addresses, phone numbers, billing information, and service usage history are all included in customer data.
Telcos can learn more about the tastes, behavior, and demographics of their consumers by employing customer data in the data mining process. For example, they may discover that particular industries have more specific communication needs or that they need a larger bandwidth. With this information, they can provide tailored services that address the particular needs of every business client.
Furthermore, consumer data assists telcos in determining possible churn issues. They can find companies that might be in danger of losing out to competitors by examining usage trends, billing information, and customer reviews. Telcos can lower churn rates and increase client retention by giving users unique incentives or proactively resolving their complaints.
Data Mining in Telecom: Driving Business Decisions
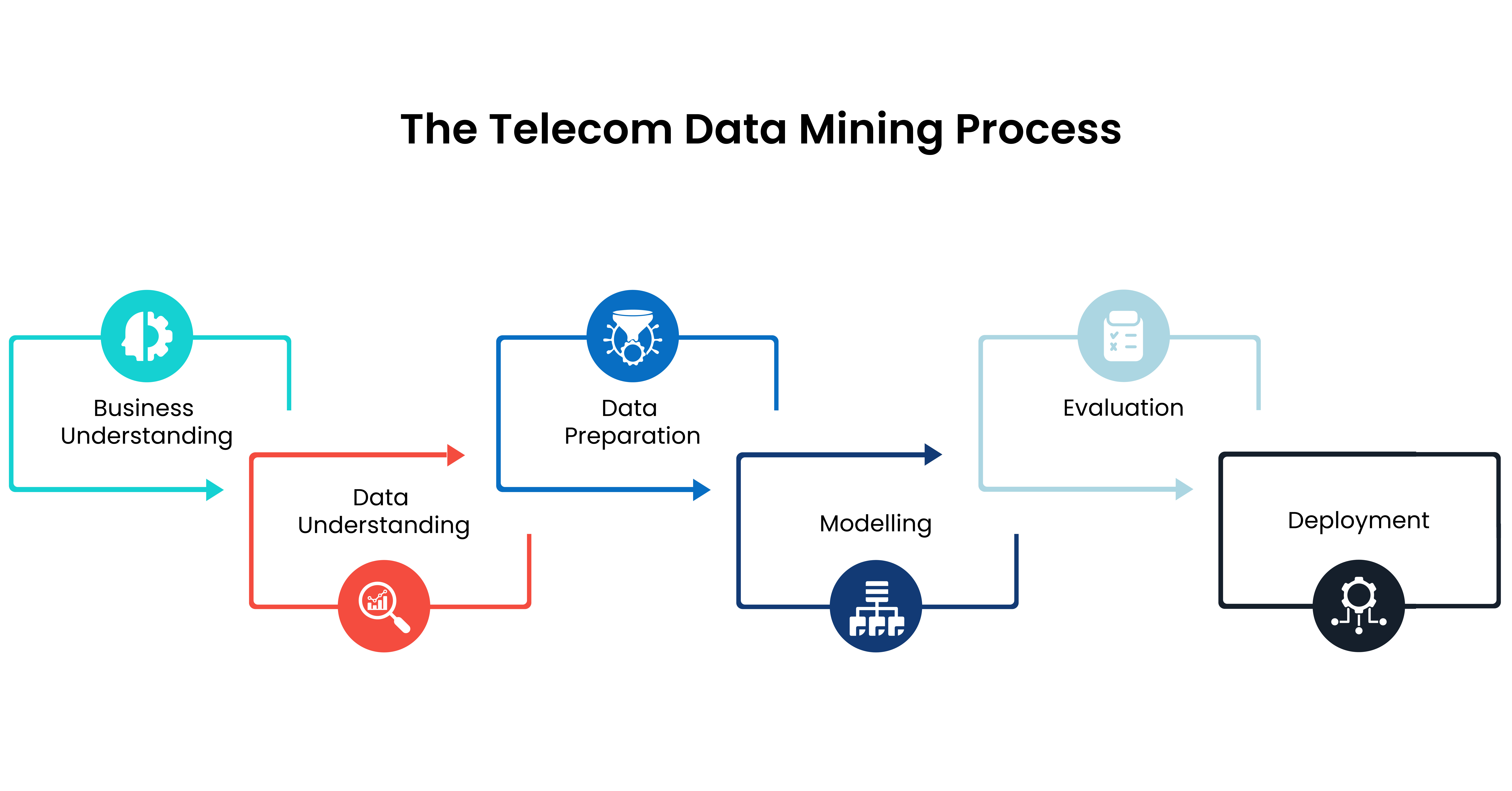
Within the telecom sector, the structured life cycle, comprising six steps, is commonly utilized to execute the data mining process. These phases entail switching back and forth based on the outcomes obtained and are frequently interconnected.
Business Understanding
You concentrate on defining the project objectives and business needs at this stage of the data mining process. To identify the data mining problem and develop a draft plan of action, you gather information. Stated differently, you translate your business requirements into targeted data mining jobs.
Data Understanding
Gaining a greater knowledge of the data you will be dealing with is aided by this stage. At this stage, you start gathering and characterizing the first dataset. You familiarize yourself with the data, spot any problems with its quality, and find some intriguing subgroups or preliminary insights that can be used to develop hypotheses.
Data Preparation
Cleaning, converting, and combining data to create the final dataset are examples of data preparation tasks in the data mining process. You gather information to identify the data mining problem and develop a draft plan of action. In other words, you translate your business requirements to targeted data mining tasks.
Modeling
The prepared data should be subjected to a variety of modeling techniques at this point in the data mining process. Predictive modeling, association rule mining, classification, and clustering are some examples of these methods. To get reliable results, you can determine the optimal values by adjusting the models’ parameters. Finding patterns, connections, or predictions in the collected data is aided by this phase.
Evaluation
After the model is developed, it is carefully examined and accessed. You carry out the required actions to build the model and make sure it complies with the company’s goals. You evaluate its dependability, accuracy, and performance. You decide whether the data mining results satisfy the expected goals based on the evaluation results.
Deployment
To extract knowledge from the data, you need to perform data mining. At this point in the process, you organize and present the knowledge to ensure that customers can easily access it. Deployment can be as simple as generating a report summarizing the findings, or as complex as implementing a repeatable data mining process across the entire organization. The goal is to make the gained insights accessible and actionable to improve decision-making and business operations.
Effective Data Mining Strategies for Optimal Results
Let’s examine the various ways that data mining techniques can be used in the telecom sector to improve customer experience, obtain insightful information, and streamline corporate processes.
Clustering
Clustering can be applied to customer segmentation. Assume a telecom company wants to find client groups that exhibit comparable behavior. Through the examination of information such as call duration, data usage, and service subscriptions, the specially designed clustering algorithm can assist in the identification of distinct customer categories, such as “Frequent Internet Users” and “Frequent Callers.” The company can develop customized offerings and focused marketing campaigns for each segment by segmenting the target audience.
Classification
Classification techniques can be used by a telecom business to anticipate client attrition. The categorization system discovers patterns linked to clients who have previously moved to a competitor by using historical data. Present clients can be divided into “Likely to Churn” and “Unlikely to Churn” groups by the algorithm based on characteristics including call duration, billing complaints, and service utilization.
Association Rule
Association rule mining is a tool telecom companies use to find cross-selling opportunities. Assume that consumer data research indicates a higher likelihood of landline phone service subscription among those who have home internet service. Utilizing this knowledge, the telecom provider can package the two services and market them to clients who have only subscribed to one of them. This tactic raises the likelihood that clients will buy the extra service.
Anomaly Detection
You can apply techniques for anomaly detection to network security. Envision a vast communication network that monitors every user’s communication habits. A user who suddenly begins producing an abnormally high volume of network traffic – well above and beyond their typical use pattern – is detected by an anomaly detection algorithm. This finding triggers a security alert since it can point to a distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack or possible network infiltration. After that, the telecom provider can immediately look into and resolve the problem.
Predictive modeling
A telecom company uses predictive modeling to forecast network traffic. By examining past data, including peak usage periods, and seasonal fluctuations, and introducing new services, the predictive model can project future network traffic patterns. This data assists the telecom provider in planning network upgrades, efficiently allocating resources, and guaranteeing peak performance during heavy demand.
Text Mining
Text mining is a tool used by telecom firms to glean insights from consumer feedback. Consider a telecom company that gets a lot of input from users via email, contact center transcripts, social media, and other methods. The business can use text mining algorithms to evaluate consumer sentiments, find recurring problems or grievances, and obtain insightful information that will help them provide better customer care.
Conclusion
The telecommunications sector was one of the first to use data mining and has implemented several applications of it. The three main uses include network monitoring, fraud detection, and marketing. Due to the magnitude of the data sets, the temporal and sequential nature of the data, and the necessity for real-time processing in many applications, the telecommunications sector faces several difficulties in data mining.
In response to these difficulties, both new and improved approaches have been created. Data mining is expected to play a significant part in the future of the telecommunications business due to the industry’s competitive and dynamic nature, as well as its massive data generation output.
Read Whitepaper Telecom’s Treasure Trove: Mining Customer Insights from Big Data
